System Integration: Best Practices for Successful Implementation
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses increasingly rely on multiple software systems to manage operations, from customer relationship management (CRM) tools to enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms. While these systems can independently streamline specific functions, integrating them effectively offers a holistic view of organizational performance, reduces redundancy, and improves operational efficiency. However, system integration comes with its challenges. Implementing best practices is crucial to ensuring a smooth and scalable integration.
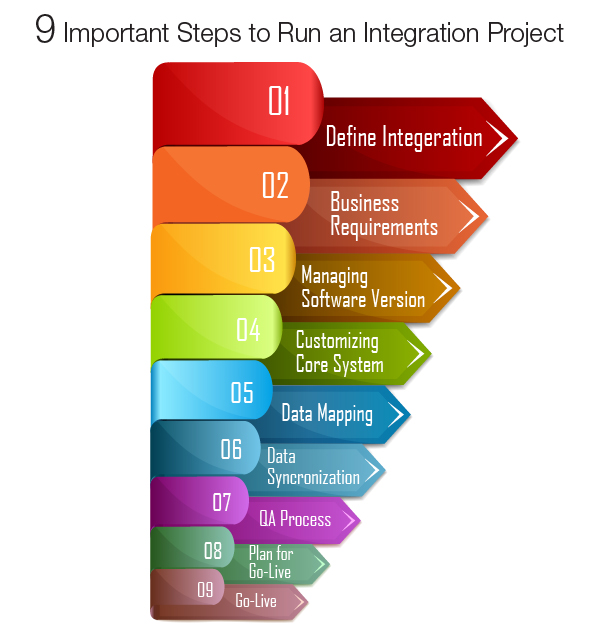
Understand the Integration Needs Before jumping into any system integration project, it’s essential to clearly understand why the integration is necessary and what goals you aim to achieve. Are you looking to streamline data flow between systems, reduce manual data entry, or provide real-time analytics? Defining the integration's scope ensures that you focus on what matters most and avoid unnecessary complications.
Choose the Right Integration Approach System integration can be accomplished using several approaches:
Point-to-Point Integration: This connects systems directly to each other. While quick to set up, it becomes difficult to maintain as the number of systems increases, often resulting in a “spaghetti architecture.”
Middleware/Enterprise Service Bus (ESB): Middleware acts as an intermediary, enabling various systems to communicate with each other. An ESB architecture is more scalable than point-to-point and can handle complex integrations involving multiple systems.
API-based Integration: Using APIs allows systems to communicate in a standardized and secure way. This method is particularly useful for cloud-based services and is widely adopted in modern integrations.
Prioritize Data Consistency and Quality Data is the core of any integration. Ensuring that data flows consistently between systems and maintaining data quality is crucial to avoid inconsistencies, errors, and duplications. Implement validation rules, error-handling mechanisms, and real-time monitoring to maintain the integrity of your data.
Security and Compliance With the increased integration of various systems, security risks also rise. Data must be encrypted during transmission and storage, and access to the systems should be tightly controlled. Ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, depending on your industry.
Ensure Scalability As your business grows, your system integration should be able to scale with it. Choose integration tools and architectures that can handle increased data flow, additional systems, and more users without compromising performance.
Test Thoroughly Before going live with the integration, it’s important to conduct thorough testing. Integration testing should include unit tests, functional tests, and stress tests to ensure that all systems communicate as expected, data flows correctly, and the entire integration performs well under heavy loads.
Monitor and Maintain System integration is not a one-time process; it requires continuous monitoring and maintenance. Regularly audit the performance of your integrated systems, watch for bottlenecks, and update your systems and integrations as necessary to ensure ongoing compatibility and efficiency.
Conclusion:
System integration is essential for businesses that want to improve efficiency, gain real-time insights, and streamline operations. By following best practices—such as defining clear objectives, ensuring data consistency, securing the integration, and planning for scalability—you can maximize the benefits while minimizing risks. Properly implemented, system integration allows your organization to function as a unified entity, driving success in a competitive market.